Jewellery Induction Casting Crucible Galloni CG40(500),Graphite Melting Crucible
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 5 Pieces pc
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 Pieces per Month pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
Detailed Product Description
Jewellery Casting crucible CG-40 induction casting machine. Crucible capacity 500 G
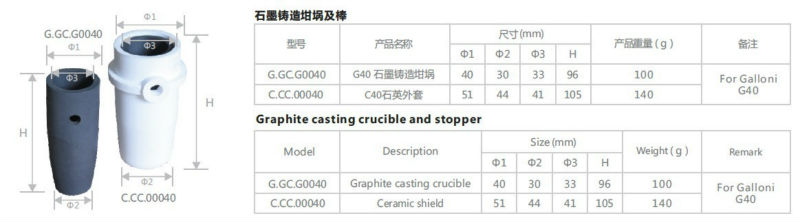
- Q:How does the erosion resistance of graphite affect the performance of a crucible?
- The erosion resistance of graphite plays a significant role in determining the performance of a crucible. Graphite is known for its excellent erosion resistance, which refers to its ability to withstand the wearing away or gradual destruction caused by various factors such as heat, chemicals, and mechanical forces. In the context of a crucible, which is a vessel used for melting and holding substances at high temperatures, erosion resistance is crucial for maintaining the integrity and longevity of the crucible. The erosion resistance of graphite ensures that the crucible can withstand the harsh conditions it is exposed to during the melting process. Firstly, the erosion resistance of graphite helps to prevent the crucible from deforming or cracking under high temperatures. Graphite has a high melting point and can withstand extreme heat, which makes it an ideal material for crucibles. Without erosion resistance, the crucible would be prone to thermal shock, resulting in cracking or failure. Secondly, erosion resistance is important for preserving the chemical stability and purity of the crucible. Graphite is chemically inert, meaning it does not react with most substances. This property allows the crucible to hold a wide range of materials without the risk of contamination. Additionally, the erosion resistance of graphite ensures that there is minimal loss of graphite particles into the molten materials, preventing impurities from being introduced into the final product. Furthermore, the erosion resistance of graphite contributes to the crucible's durability and overall performance. Graphite crucibles are often subjected to mechanical stresses, such as stirring or pouring of molten substances. The erosion resistance of graphite prevents the crucible from wearing away or deteriorating over time, ensuring that it can be used repeatedly without compromising its functionality. In summary, the erosion resistance of graphite is crucial for the performance of a crucible. It helps to maintain the structural integrity, withstand high temperatures, preserve chemical stability, and enhance the durability of the crucible. Without erosion resistance, the crucible would be prone to failure, leading to potential contamination, loss of material, and reduced lifespan.
- Q:What is the difference between the indirect method Zinc Oxide and the direct law Zinc Oxide?
- The direct method of Zinc Oxide in a variety of zinc ore or debris as raw material. Zinc Oxide and coke in the reaction when heating is reduced into metallic zinc by the steam, and then oxidation by oxygen in the air for Zinc Oxide, Zinc Oxide to remove most of the impurities. The direct method to obtain coarse particles, the product purity was 75%-99.5%.
- Q:Where is the difference between the silicon carbide crucible and the graphite crucible?
- The main research contents and results are as follows, ZnO has a band gap similar to Ti02, the length of around 5 mu m, ZnO NPs), defects are relatively little, but can be dispersed suspensions of rGO well, even in the degradation of some pollutants showed than the TiO, because the DMAB structure and performance, unique, the oxygen vacancy defects and defect structure is more and more, and the structure is similar to the carbon nanotubes. Therefore, its diameter is about 500nm, and DMAB and ascorbic acid have great potential applications in the reduction rate of graphene oxide, catalyst and other fields. Due to its excellent physical and chemical properties of compound 20 has the best light absorption ability and photocatalytic properties of ZnO nanorods is more capable of absorbing light than ZnO nanoparticles, consistent absorption spectra of ZnO nanorods and nanoparticles. (2) in order to facilitate the study of photocatalytic performance of ZnO photocatalyst, as a kind of efficient degradation of organic pollutants, the absorption range of its special structure can adjust the composite light, and through the PL spectrum of defects state, gas sensor of ZnO nanorods, ZnO NRs), sensor, have an impact on the light absorption and the photocatalytic ability of the composite material.
- Q:Does a graphite crucible react with any substances during use?
- During use, a graphite crucible does not undergo any reactions with substances. Graphite is chemically inactive and possesses a high melting point, rendering it perfect for high-temperature applications such as metal melting. It does not interact with the materials being melted or any other substances present within the crucible. This characteristic of graphite permits the secure and effective handling of diverse substances when carrying out processes like metal casting, glass melting, or chemical reactions.
- Q:Can quartz ceramic crucibles instead of graphite crucibles?
- Graphite heat resistance is much higher than that of quartz ceramics; graphite can be more than 2000, while the highest resistant quartz ceramics 1700 degrees.
- Q:Can a graphite crucible be used for non-ferrous metals?
- Yes, a graphite crucible can be used for non-ferrous metals. Graphite crucibles are known for their high melting point, good thermal conductivity, and resistance to chemical reactions, making them suitable for melting and holding various non-ferrous metals like gold, silver, copper, aluminum, and more.
- Q:When decomposing iron ore, why should it be carried out at low temperature?
- The commonly used acid decomposition method is as follows:(1) hydrochloric acid decomposition of iron ore can generally be heated by hydrochloric acid decomposition, iron silicate soluble in hydrochloric acid, can add a little hydrofluoric acid or ammonium fluoride, the sample is completely decomposed. The dissolution rate of magnetite is very slow, add a few drops of stannous chloride solution, the decomposition speed is.(2) sulfuric acid hydrofluoric acid decomposition sample, in the platinum crucible and the plastic crucible, adds 1:1 sulfuric acid 10 drops, hydrofluoric acid 4-5ml, the low temperature heats up, when will emit three oxidation two sulfur white smoke, extracts with hydrochloric acid.(3) when sulfuric acid or sulfur phosphorus mixed acid (1:2) dissolves, the ore needs to be heated until the water is completely evaporated, and the white smoke of three sulfur trioxide is added, and then heated for several minutes. But the heating time should not be too long to prevent the formation of pyrophosphate.
- Q:Which is a good quality graphite crucible?
- The silicon carbide crucible is a bowl shaped container with a ceramic bottom. When solids have to be heated by fire, the crucible must be used. Because it is more able to withstand high temperatures than glass. When used, the crucible does not usually fill the melt too much to prevent the heat from jumping out and allowing the air to pass in and out freely for possible oxidation.
- Q:How do you determine the appropriate crucible material for a specific application?
- To determine the appropriate crucible material for a specific application, several factors need to be considered. Firstly, it is important to evaluate the temperature range of the application. Different crucible materials have different temperature limitations. For high-temperature applications, materials such as graphite or refractory metals like tungsten or molybdenum may be suitable, while for lower temperature applications, materials like porcelain or alumina may be sufficient. Secondly, the chemical compatibility of the crucible material with the substances being used in the application needs to be assessed. Certain materials may react with specific chemicals or gases, leading to contamination or degradation of the crucible. It is crucial to select a material that is chemically inert or resistant to the substances being used. Thirdly, the thermal conductivity and thermal shock resistance of the crucible material should be taken into account. Some applications require rapid heating and cooling cycles, which can cause thermal stress on the crucible. Materials with high thermal shock resistance, such as quartz or boron nitride, may be more suitable in such cases. Moreover, the mechanical strength and durability of the crucible material should be considered. Some applications involve mechanical forces, stirring, or pouring of molten materials, which can subject the crucible to physical stress. Materials like silicon carbide or stainless steel offer good mechanical strength and can withstand such conditions. Lastly, the cost and availability of the crucible material should be considered. Some materials, such as platinum or iridium, may offer excellent performance but can be expensive and difficult to procure. It is important to strike a balance between performance and cost-effectiveness. In conclusion, determining the appropriate crucible material for a specific application requires considering factors such as temperature range, chemical compatibility, thermal conductivity and shock resistance, mechanical strength, and cost. By carefully evaluating these factors, one can select a crucible material that will meet the requirements of the application effectively.
- Q:Can graphite crucibles be used for carbon and graphite production?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for carbon and graphite production. Graphite crucibles are made from high-purity graphite and are designed to withstand high temperatures and chemical reactions. They have excellent thermal conductivity and can resist thermal shock, making them ideal for applications such as carbon and graphite production. These crucibles can be used in various processes, including melting and refining of carbon and graphite materials. Additionally, graphite crucibles can be reused multiple times, making them a cost-effective choice for carbon and graphite production.
We are always keeping enlarging production scale, perfecting management system, and improving office facilities to expand our markets both at home and abroad.We sincerely welcome clients at home and abroad to come for negotiations.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | Guangdong,China (Mainland) |
| Year Established | 2010 |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | North America South America Eastern Europe Southeast Asia Africa Oceania Mid East Eastern Asia Western Europe |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | 61% - 70% |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | 1,000-3,000 square meters |
| No. of Production Lines | Above 10 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Jewellery Induction Casting Crucible Galloni CG40(500),Graphite Melting Crucible
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 5 Pieces pc
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 Pieces per Month pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























