epoxy glass cloth products
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 800 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
Laminate Type ◆ 3240 G10 G11 FR-4 FR-5 ◆ Thickness:0.5mm-90mm ◆ Size:1000×1200mm 1000×2000mm 1000×2400mm Rod/Tube Type ◆ 3721 3722 3723 3724 3725 3840 3841 3520 3526 3640 ◆ Diameter:6mm 8mm 10mm-200mm ◆ Length:1000mm | |
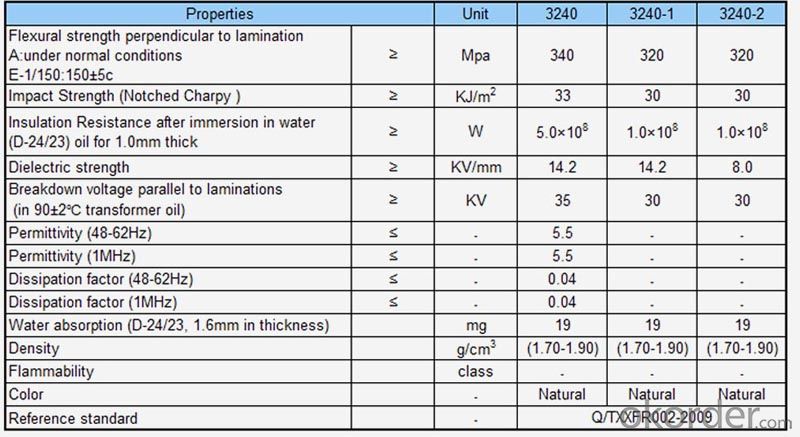
| 3240 * Temperature grade: B glass (130℃) * Color: nature, red, green, black * Thickness: 0.5-80mm * Size: 1020x2040mm | 3240-1 & 3240-2 * Temperature grade: B glass (130℃) * Color: nature,yellow * Thickness: 0.5-80mm * Size: 1020x2040mm |
 | |
| F880A F881A * Temperature grade: B glass (130℃) * Color: nature, green * Thickness: 0.5-80mm * Size(mm): 1020x1220 1020x2040 1220x2470 | F882A F883A * Temperature grade: F glass (155℃) * Color: nature, green * Thickness: 0.5-80mm * Size(mm): 1020x1220 1020x2040 1220x2470 |
- Q:Are glass fiber textiles resistant to fraying?
- Yes, glass fiber textiles are generally resistant to fraying. Glass fibers are known for their high strength and durability, which makes them less prone to fraying compared to other materials like cotton or polyester. The manufacturing process of glass fiber textiles involves weaving the fibers together tightly, creating a strong and tightly-knit fabric structure. This helps to prevent the individual fibers from becoming loose and fraying. Additionally, glass fiber textiles often have a smooth surface, further reducing the likelihood of fraying. However, it is important to note that excessive wear and tear or improper handling can still lead to minor fraying in glass fiber textiles over time.
- Q:Can glass fiber textile be used in agriculture?
- Yes, glass fiber textile can be used in agriculture. Glass fiber textiles are made from fine strands of glass that are woven together to create a flexible and durable fabric. This fabric can be used in various agricultural applications such as greenhouse construction, crop protection, and erosion control. In greenhouse construction, glass fiber textiles can be used as a covering material for the structure. The fabric is light-transmitting, allowing sunlight to penetrate while protecting the crops from harsh weather conditions. It also provides insulation, helping to maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels inside the greenhouse. Glass fiber textiles can also be used for crop protection. They can be used as insect screens, preventing pests and insects from entering the crop area. These textiles have small mesh sizes that allow air and water to pass through while keeping out unwanted intruders. Additionally, glass fiber textiles can act as a barrier against wind and hail, protecting crops from potential damage. Erosion control is another application where glass fiber textiles can be beneficial in agriculture. They can be used to stabilize soil on slopes and prevent erosion. These textiles are durable and resistant to UV radiation, ensuring long-term protection against erosion. They can be installed on hillsides, embankments, and other areas prone to soil erosion, helping to maintain the integrity of the land and protect crops. Overall, glass fiber textiles offer numerous advantages in agriculture. They are lightweight, durable, and have excellent resistance to environmental factors. With their wide range of applications, glass fiber textiles can contribute to the efficiency and sustainability of agricultural practices.
- Q:Can glass fiber textiles be used in the construction industry?
- Yes, glass fiber textiles can be used in the construction industry. Glass fiber textiles are lightweight, flexible, and have high tensile strength, making them suitable for reinforcing materials in concrete, walls, and roofs. They can also be used for thermal insulation, soundproofing, and fireproofing applications in buildings.
- Q:Are glass fiber textiles resistant to rot and decay?
- Yes, glass fiber textiles are resistant to rot and decay.
- Q:Can glass fiber textiles be used in agriculture?
- Yes, glass fiber textiles can be used in agriculture. Glass fiber textiles have several properties that make them suitable for use in the agricultural industry. Firstly, they are highly resistant to chemicals and can withstand exposure to fertilizers, pesticides, and other agricultural chemicals without deteriorating. This makes them ideal for applications such as greenhouse coverings, where they can protect crops from external elements while maintaining their integrity. Glass fiber textiles also have excellent thermal insulation properties. They can provide insulation to protect plants from extreme temperatures, helping to create a controlled environment for optimal growth. Additionally, their high tensile strength makes them suitable for use as reinforcement materials in agricultural structures such as greenhouses, tunnels, and shade nets. Furthermore, glass fiber textiles are lightweight and easy to handle, making them convenient for installation and maintenance in agricultural settings. They are also resistant to UV radiation, ensuring that they maintain their properties and longevity even when exposed to sunlight for extended periods. Overall, glass fiber textiles offer numerous benefits for agricultural applications, including chemical resistance, thermal insulation, and strength. Their versatility and durability make them a valuable choice for various agricultural needs, providing protection and support to crops in a cost-effective and sustainable manner.
- Q:How do glass fiber textiles contribute to impact absorption?
- Glass fiber textiles contribute to impact absorption by providing a strong and flexible material that can absorb and distribute the force of an impact. The fibers in the textile are able to bend and absorb energy, reducing the impact force and protecting the underlying surface or object. Additionally, the interwoven pattern of the textile helps to disperse the force of the impact, further enhancing its absorption capabilities.
- Q:Are glass fiber textiles hypoallergenic?
- Hypoallergenic is the usual classification for glass fiber textiles. These textiles are produced from inorganic materials, eliminating the presence of organic substances that could potentially induce allergies. Furthermore, glass fibers do not shed or release particles into the air, hence reducing the likelihood of allergic reactions in comparison to natural fibers like cotton or wool. Nevertheless, it is crucial to acknowledge that sensitivities can differ among individuals, and some people may still encounter allergies or irritations upon contact with glass fiber textiles.
- Q:What are the different reinforcement options for glass fiber textile?
- Depending on the desired strength and performance characteristics, glass fiber textiles have several reinforcement options available. 1. Woven Fabric: The most commonly used reinforcement option, woven fabrics interlace glass fibers in patterns such as plain or twill weaves. They offer good strength and stiffness, and find extensive use in composites, concrete reinforcements, and insulation materials. 2. Non-Woven Fabric: Unlike woven fabrics, non-woven fabrics bond or felt glass fibers together without weaving. This option provides excellent uniformity and dimensional stability, making it suitable for filtration media, geotextiles, and thermal insulation. 3. Chopped Strand Mat (CSM): CSM is formed by randomly aligning short glass fibers in a binder material matrix. It offers good strength, easy handling, and the ability to mold into complex shapes. It is commonly utilized in boat building, automotive parts, and corrosion-resistant tanks. 4. Continuous Roving: Continuous roving is a bundle of untwisted glass fibers that provides high tensile strength. It is specifically used for applications requiring exceptional strength, like wind turbine blades, pressure vessels, and aerospace components. 5. Knitted Fabric: Knitted fabrics interlock loops of glass fibers, granting them flexibility and conformability. This makes them suitable for applications that necessitate stretchability, such as sports equipment, medical products, and clothing. 6. Multiaxial Fabrics: Multiaxial fabrics arrange glass fibers in multiple layers or orientations, including unidirectional, biaxial, or triaxial layers. This option offers tailored mechanical properties, improved strength in specific directions, and enhanced impact resistance. It is commonly employed in aerospace structures, automotive parts, and high-performance sports equipment. Manufacturers and designers have a range of choices with these reinforcement options, allowing them to select the most suitable option based on specific requirements for strength, flexibility, conformability, and other performance characteristics.
- Q:Can glass fiber textiles be printed?
- Glass fiber textiles have the capability to undergo printing. They possess adaptability and can be printed through a range of techniques like screen printing, digital printing, and transfer printing. These methods enable the addition of designs, patterns, or images to the glass fiber textiles, thereby enhancing their visual appeal and practicality. To ensure proper adhesion and colorfastness, it may be necessary to utilize specific inks or dyes that are compatible with glass fibers during the printing process. Moreover, achieving the desired outcome necessitates considering the heat resistance and durability of glass fiber textiles.
- Q:What are the environmental impacts of glass fiber textile production?
- There are several environmental consequences associated with the production of glass fiber textiles. First and foremost, a significant amount of energy is required to produce these materials, often obtained from non-renewable fossil fuels. This energy consumption contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Moreover, the manufacturing process of glass fiber textiles involves the utilization of various chemicals, such as resins, binders, and solvents. If not properly managed, these chemicals can pose a threat to both human health and the environment. They have the potential to contaminate air, water, and soil, leading to pollution and potential ecological damage. Additionally, the production of glass fiber textiles necessitates the extraction and processing of raw materials like silica sand, limestone, and soda ash. This extraction process can result in habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. Furthermore, it can deplete natural resources, particularly as the demand for glass fiber textiles continues to rise. Lastly, the disposal of glass fiber textiles at the end of their lifecycle presents another environmental challenge. Unlike natural fibers, glass fibers do not easily degrade and can persist in the environment for an extended period. Improper disposal can lead to accumulation in landfills, exacerbating waste management issues. To address these environmental impacts, manufacturers must adopt cleaner production techniques, such as utilizing renewable energy sources and reducing the use of hazardous chemicals. Recycling and reusing glass fiber textiles can also help minimize waste and conserve resources. Additionally, it is crucial to promote sustainable consumption patterns and raise awareness among consumers about the environmental consequences of glass fiber textiles, thereby encouraging responsible production and consumption practices.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
epoxy glass cloth products
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 800 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























